Criteria for Evaluating Top HDI PCB Manufacturers
.png?resizemode=force&maxsidesize=500)
This guide explains how to evaluate top HDI PCB manufacturers for high-density, high-reliability rigid PCB designs. It is written for PCB design engineers, hardware teams, and sourcing managers selecting an HDI partner for prototype, NPI, or production builds. The criteria focus on HDI process capability, quality certifications, and reliability controls required to support microvia-based designs.
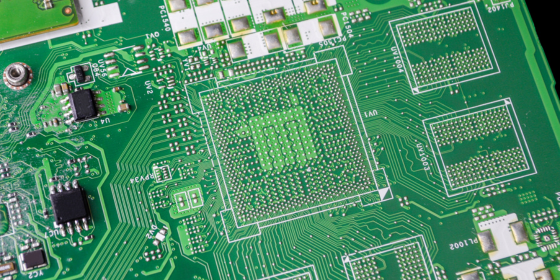
High-density interconnect printed circuit boards use laser-drilled microvias, thin dielectrics, and fine line and space geometries to achieve dense routing with controlled impedance and low signal loss. HDI rigid PCBs rely on stacked, staggered, blind, and buried microvias to shorten signal paths and preserve signal integrity in space-constrained, high-speed electronics.
Industry guidance for HDI design and fabrication is defined by IPC under IPC-2226, which specifies microvia structures, layer stacking, dielectric control, and impedance requirements. Alignment with this standard is foundational when comparing HDI PCB manufacturers.
What Defines a High-Quality PCB Manufacturer?
Quality systems and certifications
Quality systems and certifications are the foundation of a dependable HDI partner. Top HDI PCB manufacturers demonstrate conformance to IPC-A-600 and IPC-6012 for rigid boards, supported by ISO 9001 quality systems. Application-specific programs require IATF 16949 for automotive, ISO 13485 for medical devices, and AS9100 for aerospace. Advanced suppliers also provide UL recognition, RoHS and REACH compliance, full traceability, and documented reliability testing such as IST, CAF, and thermal shock.
IPC-A-6012 (Qualification and Performance Specification for Rigid Printed Boards) provides the baseline for evaluating the quality of HDI rigid PCBs, with a particular focus on dimensional stability, material quality, and process consistency.
HDI process and technology capability
TLeading manufacturers support laser-drilled microvias down to 75 µm or smaller, stacked microvia structures, sequential lamination, resin-coated copper, and mSAP for ultra-fine lines. Mature HDI facilities use laser direct imaging, automated optical inspection, X-ray inspection, and controlled impedance verification. Experience with low-loss materials such as Megtron 6, Tachyon, and I-Speed is critical for high-speed designs.
Reliability, scalability, and execution
The best HDI PCB partners deliver predictable lead times, high yields, and consistent on-time delivery. Multi-site redundancy, quick-turn prototyping, early DFM engagement, and clear pathways from NPI to volume production are key indicators of long-term manufacturability.
Leading HDI PCB Manufacturers in 2026
Across North America, Europe, and Asia, best-in-class HDI manufacturers share common process practices. These include laser direct imaging for sub-50 µm line and space geometries, optimized chemistries for high-aspect-ratio microvia plating, robust stacked and skip-via strategies, and mSAP for ultra-fine features.
Integrated inspection and test coverage, such as CT X-ray for microvia integrity, is standard among advanced facilities. IPC-2226 recommends X-ray inspection for stacked microvia structures to verify interconnect reliability in high-density designs.
Representative outcomes include smartphone mainboards with line and space below 50 µm, automotive radar modules built on low-loss laminates for stable high-frequency performance, aerospace avionics produced through multi-step sequential lamination, and networking hardware requiring tight impedance control across high layer counts.
IPC-2226 also recommends that manufacturers utilize X-ray inspection for microvia integrity, especially when stacked vias are involved in high-density designs, ensuring long-term reliability and signal integrity in mission-critical applications.
Examples of outcomes include smartphone mainboards with line/space below 50 µm using mSAP, automotive radar modules utilizing low-loss laminates for stable high-frequency behavior, and aerospace avionics produced through multi-step sequential lamination that supports reliable microvia stacking. In networking, HDI backplanes and midplanes demonstrate tight impedance control across high layer counts, underscoring process discipline and material expertise typical of top electronic circuit boards manufacturers and circuit board manufacturing companies.
Matching the Manufacturer to the Application
HDI manufacturer selection should align with end-use requirements. Consumer electronics programs prioritize fine-feature capability, yield, and speed. Automotive and aerospace programs demand certifications, traceability, and validated reliability testing. Networking, 5G, and data center designs require deep materials expertise and consistent impedance control across production lots.
Common Applications for HDI Rigid PCBs
HDI rigid PCBs are widely used in smartphones, wearables, automotive ADAS and radar modules, medical imaging systems, aerospace avionics, 5G and networking hardware, industrial automation, and high-performance computing. These applications demand fine features, controlled impedance, and proven interconnect reliability.
What to Ask Prospective HDI PCB Manufacturers
- What are your qualified microvia sizes, stacked via limits, and minimum line and space?
- Which HDI materials and low-loss laminates are production-qualified?
- What reliability testing is performed on stacked and blind microvia structures?
- How do you support stackup engineering, impedance modeling, and DFM before layout release?
- What are typical lead times and yield performance from prototype through volume?
_______________________________
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Which certifications should I prioritize for HDI production? IPC-6012, IATF 16949 for automotive, ISO 13485 for medical, AS9100 for aerospace, UL recognition, and RoHS/REACH compliance. These signal process maturity and regulatory readiness across circuit board suppliers and circuit board manufacturing companies.
-
How do I confirm a supplier’s HDI capability? Ask for detailed capability matrices, sample stackups, reliability test reports, and yield data. A design review with the CAM team will reveal practical manufacturability limits, especially for HDI rigid PCBs.
-
What lead times are typical for HDI? Quick-turn prototypes often run 5–15 business days depending on complexity and materials. Production cycles usually span 3–6 weeks, longer for exotic laminates or multi-step sequential lamination among electronic circuit boards manufacturers.
-
Are mSAP and laser drilling necessary for all HDI? No. Conventional HDI with laser-drilled microvias and sequential lamination covers most needs. mSAP is ideal for sub-50 µm line/space or aggressive miniaturization, a capability you’ll find among who are the top HDI PCB manufacturers and leading PCB board suppliers.
-
How do I manage cost on HDI boards? Optimize stackup early, minimize unnecessary build-up layers, align via structures with routing needs, choose readily available low-loss materials, and engage DFM to reduce rework and improve yields.
Related Posts

Beyond ISO 9001: Why AS9100D is the Right Quality Standard for Your Aerospace PCBs

Certifications for Military PCBs: What Aerospace and Defense Design Engineers Need to Know
.png?resizemode=force&maxsidesize=1226)